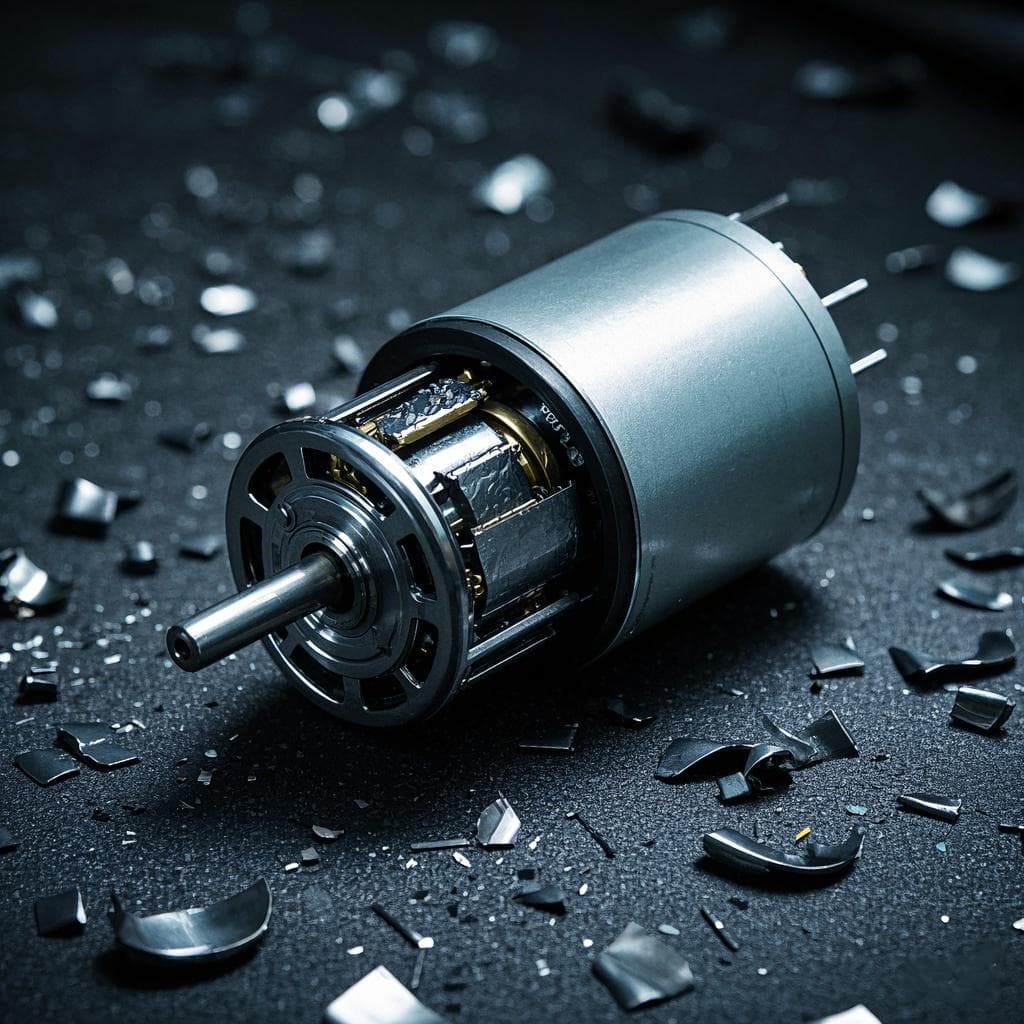
Hollow Cup Motor is a special type of motor, named after its hollow rotor. Unlike traditional motor design, the rotor of the hollow cup motor is shaped like a cup with a hollow center. Hollow Cup Motor is widely used in applications with high requirements for size, weight, efficiency and response speed due to its unique design, high efficiency, low inertia and fast response. Especially in drones, robots, optical equipment, medical equipment, small wind turbines.
The working principle of hollow cup motor is similar to that of traditional brushless DC motor (BLDC). They usually consist of a stator and a rotor:
- Stator: The stator usually consists of a set of windings and permanent magnets. The stator generates a rotating magnetic field when it is running, driving the rotor to move.
- Rotor: The rotor is usually made of a thin conductive material (such as copper) and has a hollow structure. The hollow design makes the rotor lighter, has less inertia and responds faster. There is not necessarily a permanent magnet inside the rotor, but in some designs, the rotor may also have built-in permanent magnets.
- External control system: Coreless motors usually require an external electronic controller (ESC, Electronic Speed Controller) to manage the supply of current and voltage to ensure efficient operation of the motor.
The permanent magnets in coreless motors are generally NdFeB permanent magnets. This is because it has a very high magnetic energy product (high magnetic density) and can provide a strong magnetic field, which is very suitable for occasions such as coreless motors that require high efficiency and high power density. The use of NdFeB magnets can enable the motor to provide more power in a smaller volume.
The NdFeB magnets in coreless motors are generally square, tile-shaped, or ring-shaped (multi-pole magnetization). Depending on the motor design, our company can customize the shape and tolerance according to customer requirements. It is worth noting that different grades of NdFeB magnets have different operating temperatures. In order to ensure the normal operation of coreless motors in high temperature environments, NdFeB magnets are usually required to be able to operate at temperatures of 80°C to 150°C or higher. For special applications, such as drone motors, industrial automation and other fields, it may be necessary to use high-temperature NdFeB magnets with a temperature resistance of up to 200°C.