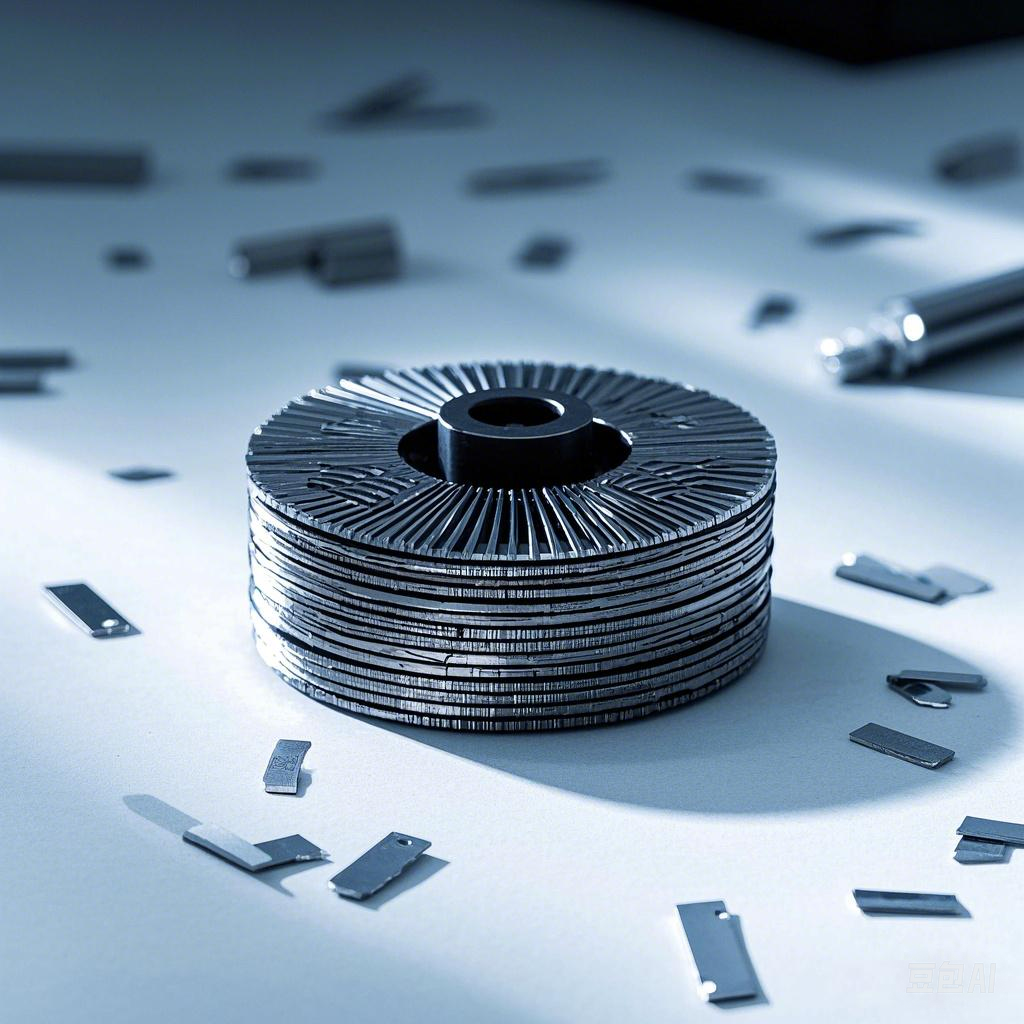
The following are the general steps for manufacturing laminated magnets:
Material Preparation
- Thin Sheets of Magnetic Materials
- Select appropriate magnetic materials, such as neodymium iron boron (NdFeB), ferrite, etc. The thickness of these thin sheets usually ranges from 0.1 to 1 mm, depending on the application requirements. For example, in high-frequency application scenarios, thinner sheets may be chosen to further reduce eddy current losses. Neodymium iron boron thin sheets have relatively high magnetic properties, while ferrite thin sheets have lower costs and good chemical stability.
- Insulating Materials
- Prepare insulating coating materials or insulating spacers. If it is a coating material, epoxy resin coating is commonly used, which can be applied to the surface of magnetic sheets by spraying or dipping. Insulating spacers can be made of polyester film, polyimide film, etc. Their thickness is very thin, usually ranging from a few micrometers to dozens of micrometers, and they are used to isolate magnetic sheets and block the paths of eddy currents.
- Bonding Materials (Optional)
- Depending on the specific forming method, bonding materials may be required. For example, epoxy glue can be used to bond magnetic sheets together to ensure the stability of the laminated structure. The selected glue should have good bonding performance and certain temperature resistance to adapt to the working environment of the magnetic steel.
- Molds (Optional)
- If you want to make laminated magnets with specific shapes, you need to customize appropriate molds. The material of the mold can be metal (such as steel) or high-strength plastic, and its shape should match the final shape of the required magnet, which is used to shape the magnetic sheets during the laminating and forming processes.
Treatment of Magnetic Sheets
- Surface Cleaning
- Before laminating, the thin sheets of magnetic materials need to be cleaned to remove impurities such as oil, dust, and oxides on the surface. You can wipe the surface of magnetic sheets with an organic solvent (such as acetone or ethanol) and then dry them with clean non-woven fabric. This step is very important because impurities may affect the insulation effect between magnetic sheets and the bonding quality.
- Insulation Treatment
- If using an insulating coating, immerse the magnetic sheets in the insulating paint, then slowly take them out, let the excess paint drip off naturally, and then put them into an oven to dry. The drying temperature and time depend on the characteristics of the paint. Generally, they are dried at 100 – 150 °C for 1 – 2 hours to make the coating cured.
- If using insulating spacers, cut the spacers into the same shape as the magnetic sheets or slightly larger, and then place the spacers between the magnetic sheets to ensure that they completely cover the surface of the magnetic sheets and play an insulating role.
Laminating Process
- Manual Laminating (Suitable for Small Batches or Simple Shapes)
- Stack the treated magnetic sheets one by one. During the stacking process, make sure that the direction of the magnetic sheets is correct to obtain the desired magnetic field direction. If a specific magnetic field distribution is required, the magnetic sheets can be laminated according to the pre-designed arrangement method, for example, stacking magnetic sheets with different magnetization directions alternately. Meanwhile, make sure that the insulating materials between the magnetic sheets are properly placed to prevent direct contact between magnetic sheets and the generation of eddy currents.
- Mechanical Laminating (Suitable for Mass Production)
- Use automated equipment for laminating, such as robotic arms with suction cups or fixtures. The robotic arms can accurately pick up magnetic sheets according to the preset program and place them at the stacking position. This method is efficient and accurate and can ensure the quality and consistency of laminating. During the laminating process, attention should also be paid to the insulation and arrangement of magnetic sheets.
Forming and Fixing (Optional)
- Pressure Forming
- If you need to make the laminated magnets into specific shapes, you can put the laminated magnetic sheets into a mold and then apply a certain amount of pressure. The magnitude of the pressure depends on the material and quantity of the magnetic sheets, usually ranging from several tons to dozens of tons. Under the action of pressure, the magnetic sheets will be compressed and conform to the shape of the mold to form the required shape of the magnetic steel. Meanwhile, the bonding material (if used) will better fill the gaps between the magnetic sheets under pressure and enhance the integrity of the laminated structure.
- Curing and Bonding (If Bonding Materials Are Used)
- Place the formed laminated magnets in an appropriate environment to allow the bonding material to fully cure. The curing temperature and time are set according to the requirements of the bonding material. For example, some epoxy glues need to be cured at room temperature for 24 hours or at a higher temperature (such as 60 – 80 °C) for several hours to achieve the best bonding strength.
Post-treatment
- Surface Treatment (Optional)
- Depending on the application requirements, the surface of the laminated magnets can be further treated. For example, electroplating treatment, such as nickel plating or zinc plating, can be carried out to improve the corrosion resistance and appearance quality of the magnetic steel. The thickness of the electroplating layer is usually between a few micrometers and dozens of micrometers, and the specific thickness is determined according to the protection requirements and application environment.
- Performance Testing
- Use a Gauss meter and other equipment to test the performance indicators such as magnetic field strength and magnetic field distribution of the laminated magnets to ensure that they meet the design requirements. If it is found that the magnetic field performance does not meet expectations, it is necessary to check whether there are problems in the laminating process, such as incorrect arrangement of magnetic sheets or poor insulation, and make corresponding adjustments or remake them.