Introduction
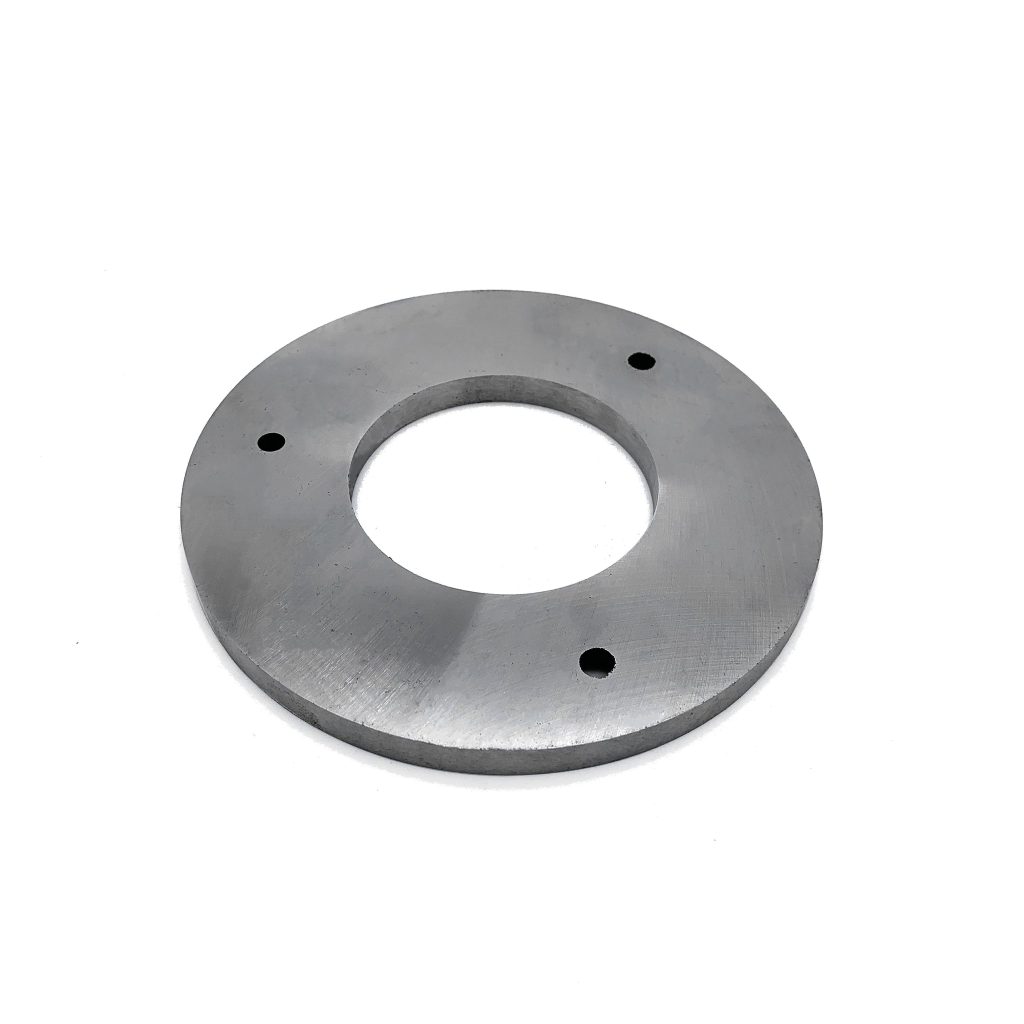
In the vast landscape of magnetic materials, Alnico magnets stand as a testament to the harmonious blend of historical significance, remarkable properties, and widespread applications. Derived from a combination of aluminum (Al), nickel (Ni), cobalt (Co), and often including iron (Fe) and/or copper (Cu) in varying proportions, Alnico magnets have been a cornerstone of the magnetic industry since their inception in the early 1940s. Their unique characteristics make them an ideal choice for numerous applications requiring high magnetic strength, good temperature stability, and exceptional corrosion resistance.
History and Development
The history of Alnico magnets can be traced back to the quest for stronger and more stable magnetic materials during World War II. As the demand for high-performance magnetic components surged for use in military technologies and electronics, researchers focused on developing alloys that could surpass the limitations of traditional magnetic materials like ferrite. The resulting Alnico alloys not only surpassed these expectations but also established themselves as a reliable alternative to rare earth magnets in many applications due to their abundant raw materials and cost-effectiveness.
Key Properties
1. High Magnetic Strength: Alnico magnets are known for their strong magnetic fields, rivaling even some rare earth magnets in terms of residual induction (Br) and energy product (BHmax). This makes them particularly suitable for applications where high magnetic pull forces are essential.
2. Temperature Stability: Unlike many other magnetic materials, Alnico maintains its magnetic properties over a wide range of temperatures, making it an excellent choice for high-temperature environments. This stability is crucial in applications like automotive engines, aerospace components, and industrial machinery where heat is a significant factor.
3. Good Corrosion Resistance: The metallic composition of Alnico alloys grants them inherent resistance to corrosion, ensuring long service life even in challenging environments.
4. Demagnetization Resistance: With a relatively high coercivity (Hcb), Alnico magnets are less susceptible to accidental demagnetization caused by external magnetic fields or mechanical shocks.
Applications
– Automotive Industry: Alnico magnets are widely used in automotive applications, including motor assemblies, sensors, and actuators, owing to their high temperature stability and durability.
– Electronics and Communications: They find applications in speakers, microphones, and various electronic devices, leveraging their strong magnetic fields to enhance performance.
– Medical Equipment: Their corrosion resistance and biocompatibility make Alnico magnets suitable for use in medical devices like MRI machines and implants.
– Aerospace and Defense: The demanding conditions of aerospace and defense applications call for magnetic materials that can withstand extreme temperatures and resist demagnetization. Alnico fits this bill perfectly, with its robust properties enabling reliable performance in critical systems.
– Scientific Research: Researchers often employ Alnico magnets in experiments requiring precise magnetic fields, taking advantage of their stability and controllability.
Alnico magnets, with their blend of strength, durability, and versatility, continue to play a pivotal role in various industries. From their historical significance as pioneers of high-performance magnetic alloys to their modern-day applications in diverse fields, Alnico magnets demonstrate the enduring value of innovation and adaptation. As technology evolves, so too will the applications of these remarkable magnetic materials, ensuring that the legacy of Alnico endures for generations to come.